Table of Contents
Introduction
The world is at a critical point, seeking sustainable solutions to combat climate change and reduce our carbon footprint. Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a significant player in this pursuit, offering a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. While the adoption of EVs has been on the rise, the concept of bi-directional EV charging has emerged as a game-changing technology that could revolutionize the way we think about energy management and grid stability. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies and workings of bi-directional EV charging, exploring its benefits, challenges, and its potential impact on our energy landscape.
Understanding Bi-Directional EV Charging
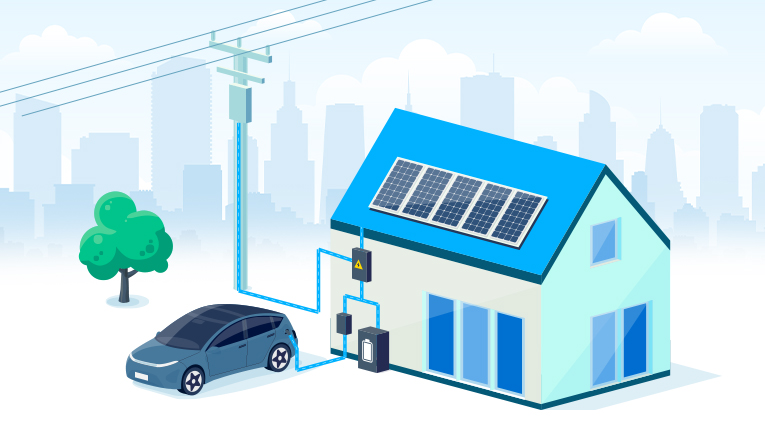
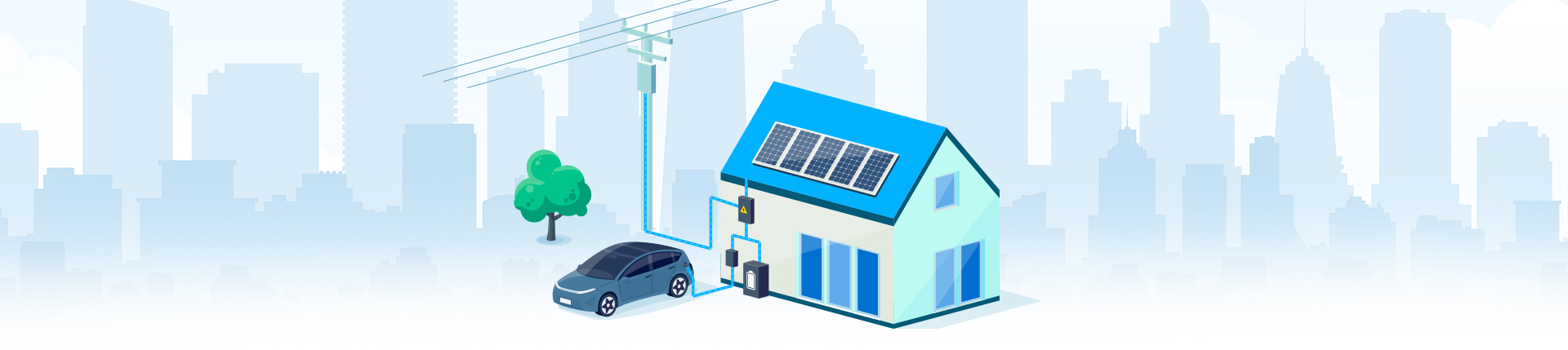
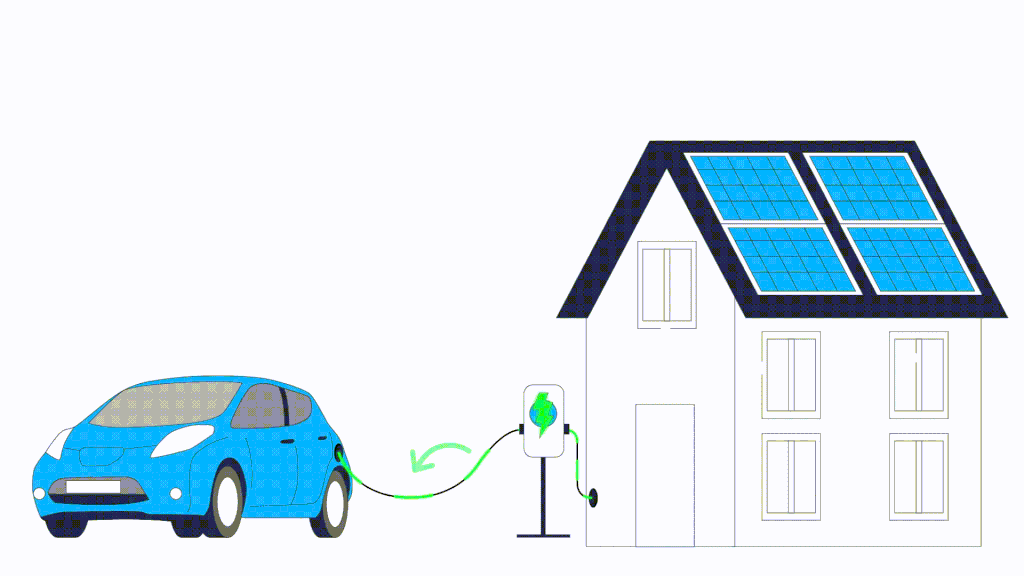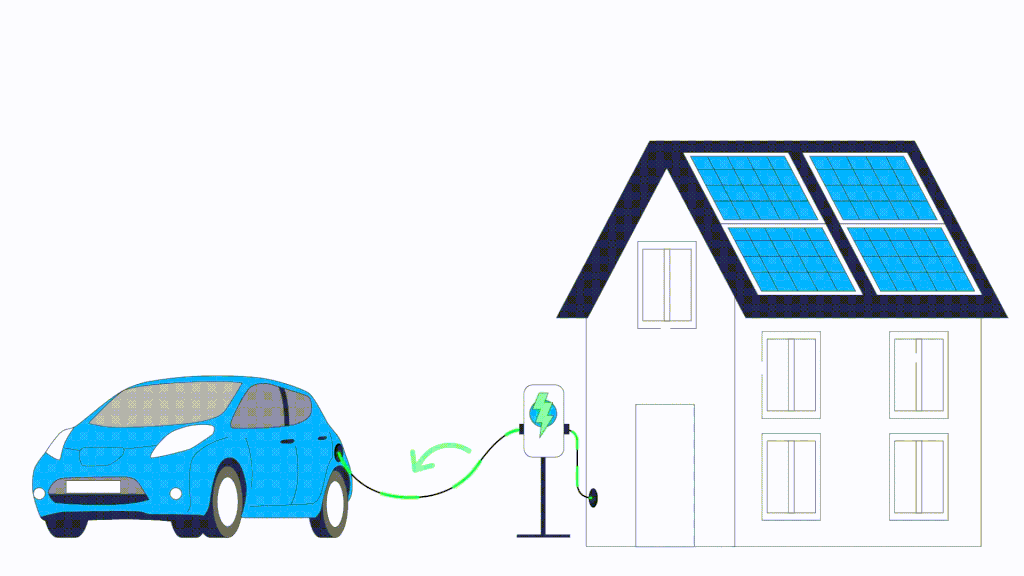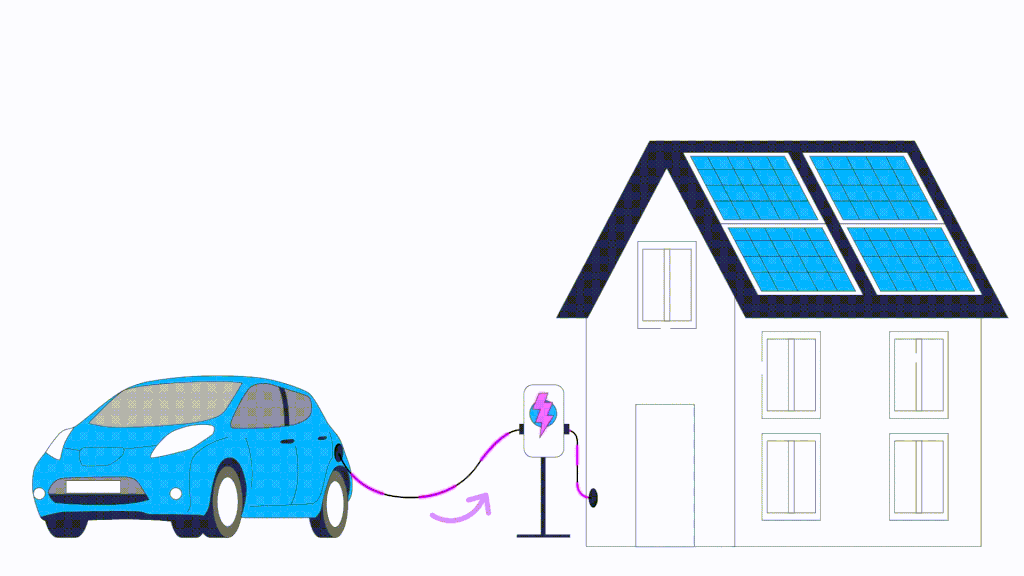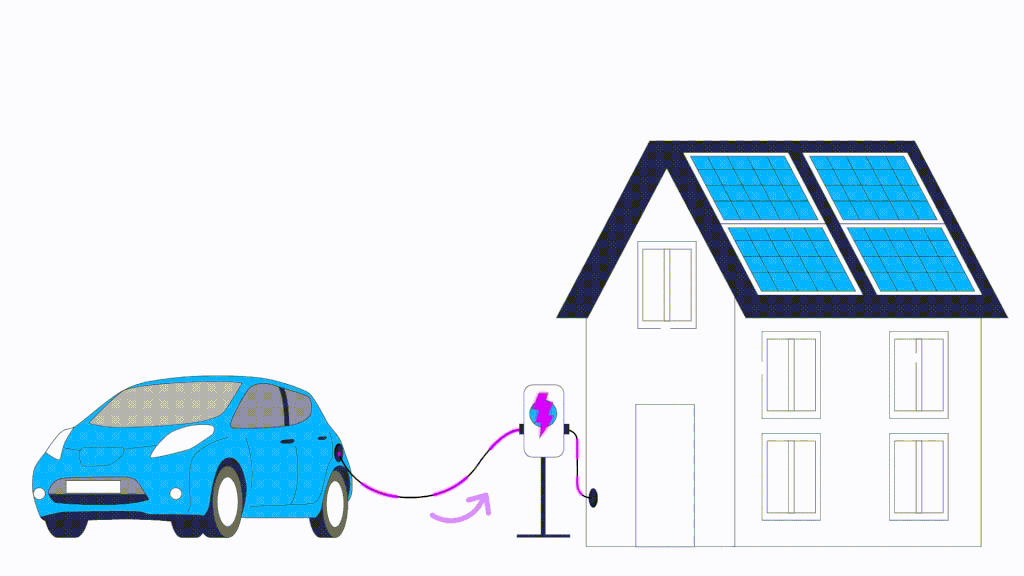
Traditional electric vehicle charging involves drawing energy from the grid to charge the vehicle’s battery. Bi-directional EV charging, also known as V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) technology, takes this concept a step further from the traditional one-way flow of electricity. While the traditional charger allows the electricity to flow from the grid to the vehicle battery, bi-directional chargers enable a two-way exchange of energy. Bi-directional EV chargers work by converting the Direct Current (DC) power stored in the EV battery into Alternating Current (AC) electricity This means that not only can you charge your EV from the grid, but your EV vehicle can also feed excess energy back into the grid or power your home during energy outages.
Benefits of Bi-Directional EV Charging
- Grid Stabilization: One of the key advantages of bi-directional EV charging is its potential to stabilize the electric grid. EVs can absorb surplus energy during periods of high generation and feed it back during peak demand, thus helping to balance supply and demand fluctuations.
- Emergency Power: In the case of power outages or emergencies, bi-directional EV charging could provide a backup power source for homes, hospitals, and other critical facilities. EVs could act as distributed energy resources, enhancing the resilience of the energy system.
- Demand Response: With bi-directional charging, EV owners could respond to price signals and grid needs by adjusting their charging patterns. This could incentivize charging during off-peak hours and discharging during peak demand, resulting in cost savings for EV owners and reduced strain on the grid.
- Renewable Integration: The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind can be mitigated with bi-directional EV charging. Excess energy generated during sunny or windy periods can be stored in EV batteries and released back to the grid when generation is low.
Challenges and Considerations
- Battery Degradation: The process of frequent charge and discharge cycles can impact the lifespan of EV batteries. Implementing proper battery management systems and algorithms is essential to mitigate degradation.
- Regulation and Standards: Establishing uniform regulations and standards for bi-directional charging is crucial to ensure interoperability, safety, and effective grid integration across different vehicle manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers.
- Cybersecurity: As EVs become more integrated into the energy ecosystem, cybersecurity becomes a paramount concern. Ensuring the security of communication between vehicles, chargers, and the grid is essential to prevent potential breaches.
- Infrastructure Investment: Bi-directional charging requires a robust charging infrastructure capable of handling bidirectional power flows. Investment in both vehicle and grid infrastructure is necessary for the widespread adoption of this technology.
Future Prospects and Implications
Bidirectional EV charging represents a significant leap forward in the integration of sustainable energy solutions. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see wider adoption of bidirectional charging infrastructure and further refinement of the associated technologies.
Many leading automobile manufacturers have shown interest in Bi-directional charging and confirmed their models will have Bi-directional EV charging capability in the coming future. In a few of the countries, testing has also started of V2G technology on a larger scale, using EVs to stabilize the grid and provide frequency regulation.
In a nutshell, bidirectional EV charging not only transforms the way we charge our vehicles but also empowers them to be active participants in the broader energy ecosystem. With the potential to stabilize grids, increase energy resilience, and maximize the utilization of renewable resources, this technology is poised to play a pivotal role in the sustainable future of transportation and energy.
By embracing bidirectional charging, we are not only charging our vehicles but also charging towards a greener and more sustainable tomorrow.
How Does VVDN Help EV Charger OEMs?
VVDN leverages its vast expertise in the complete design, development, and manufacturing including certifications, of EV charging solutions, including AC Chargers, DC Chargers, and Bi-directional EV Chargers. and is a leading electric vehicle charger manufacturer for global OEMs who are looking to add the same in their product line. VVDN’s testing facilities and experienced engineers make 100% sure that the product meets all the required safety standards.
Click Here to know more about VVDN EV charging solution offerings or write to us at info@vvdntech.com.